Genome-Wide Association Study for Spike Traits and Distribution of Two QTLs for Grain Number in Chinese Wheat Cultivars
Abstract
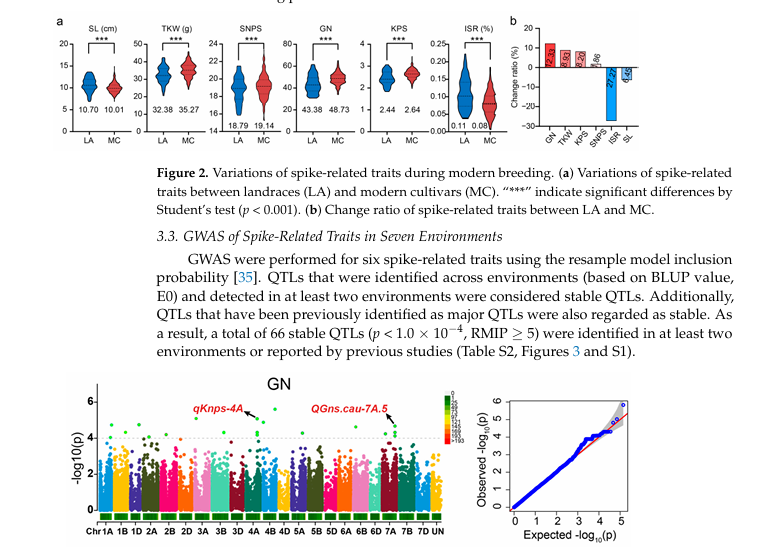
Spike traits play an important role in improving wheat yield. However, the application of reported spike-related loci remains unclear. Here, we assessed six spike-related traits across seven different environments using 406 wheat accessions. A negative correlation was observed between two components of wheat yield: thousand kernel weight (TKW) and grain number per spike (GN). Nonetheless, TKW and GN were significantly higher in modern cultivars compared to landraces. Tworeliable quantitative trait loci (QTLs) related to GN, QGN.nwafu-4A and QGN.nwafu-7A, were identified through genome-wide associate analysis. QGN.nwafu-4A showed pleiotropy on GN, kernel number per spikelet and spike length. Both elite haplotypes of QGN.nwafu-7A were prominently present in Chinese modern cultivars, particularly those released after the year 2000. Elite haplotype AofQGN.nwafu-7A was significantly prevalent in Chinese Yellow and Huai wheat zone, while elite haplotype D of QGN.nwafu-7A was concentrated in other wheat-growing regions of China.